Onion Nutrition facts
Onion is one of the oldest edible food ingredients known to humankind used in a bewildering array of recipes and preparations, be it your favorite salad or a mouth-watering gravy or curries! It has also been employed in traditional medicines since ancient times for its health-promoting and curative properties.
Botanically, onions are members of the Alliaceae family, in the genus, Allium and known scientifically as Allium cepa.
 |
Onion is a small herb plant that grows to about 2 feet tall. In the botany, its underground globular bulb is a stem that consists of fleshy, modified leaves arranged in whorls. There are many cultivar varieties of onions grown around the world. On average, the crop takes about three to four months from seedlings to harvest. Top greens or scallions and flower heads are also eaten all around the world.
The Sharp, pungent smell of onion is due to its sulfur compound, allyl propyl disulfide. Spanish red onions generally possess less of this compound and therefore mild-flavored than white or brown varieties. This characteristic of Spanish variety would make them ideal for use in raw salads.
Vidalia onions (Georgia sweet, yellow granex) are popular varieties grown for their sweet, mild flavor. Its farming is restricted to certain counties in the South-Eastern region of Georgia state in the USA where climate and low sulfur soil conditions are most suitable for the uniqueness of the crop.
Cipolle di Tropea (red onions of Tropea) are large, torpedo fish-shaped onions grown around the Tropea region in Calabria province of Southern Italy. These onions are popular for their strong, pungent flavor.
Shallot (Allium cepa L. var. aggregatum) is a type of onion that produces a cluster of small-elongated bulbs from a single plant. Shallots are relatively smaller, less pungent, and taste sweeter than onions.
Find the below infographic- Differnces between onions and shallots
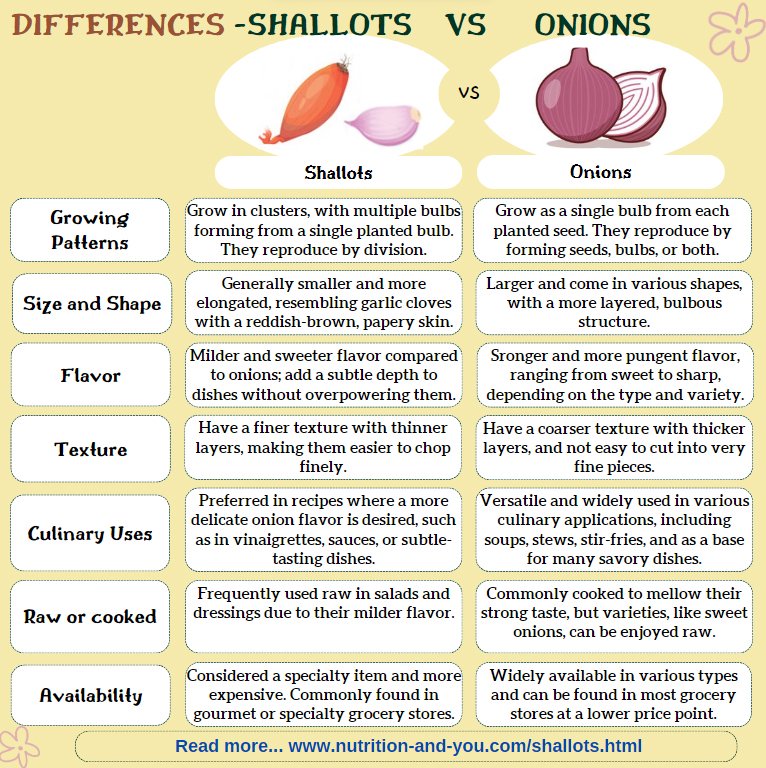 |
Health Benefits of Onions
Onions are very low in calories and fats. 100 grams carry just 40 calories. However, rich in soluble dietary fiber.
The phytochemical compounds allium and Allyl disulfide in the onions convert into allicin by the enzymatic reaction when its bulb (modified leaves) are distorted (crushing, cutting, etc.). Studies have shown that these compounds have anti-mutagenic (protects from cancers) and anti-diabetic properties (helps lower blood sugar levels in diabetics).
Laboratory studies show that allicin reduces cholesterol production by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase enzyme in the liver cells. Further, it also found to have antibacterial, antiviral, and anti-fungal activities.
Additionally, Allicin also decreases blood vessel stiffness by facilitating the release of nitric oxide (NO) and thereby bring a reduction in the total blood pressure. Further, it blocks platelet clot formation and has fibrinolytic action (clot breakdown) in the blood vessels and thereby prevents blood clots from growing and becoming problematic. Altogether, it helps decrease in overall risk of coronary artery disease (CAD), peripheral vascular diseases (PVD), and stroke.
Onions are a rich source of chromium, a trace mineral that helps tissue cells respond appropriately to insulin levels in the blood. It thus helps facilitate insulin action and control sugar levels in diabetes.
They are also a good source of antioxidant flavonoid quercetin, which is found to have anti-carcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, and antidiabetic functions.
They are also good in antioxidant vitamin, vitamin-C and mineral manganese. Manganese is essential as a co-factor for the anti-oxidant enzyme, superoxide dismutase. Also, isothiocyanate antioxidants in them help provide relief from cold and flu by exerting anti-inflammatory actions.
Onions are also good in the B-complex group of vitamins like pantothenic acid, pyridoxine, folates, and thiamin. Pyridoxine or vitamin B-6 helps keep up GABA levels in the brain, which works against neurotic conditions.
| Principle | Nutrient Value | Percent of RDA |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 40 Kcal | 2% |
| Carbohydrates | 9.34 g | 7% |
| Protein | 1.10 g | 2% |
| Total Fat | 0.10 g | 0.5% |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg | 0% |
| Dietary Fiber | 1.7 g | 4.5% |
| Vitamins | ||
| Folates | 19 µg | 5% |
| Niacin | 0.116 mg | 1% |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.123 mg | 2.5% |
| Pyridoxine | 0.120 mg | 9% |
| Riboflavin | 0.027 mg | 2% |
| Thiamin | 0.046 mg | 4% |
| Vitamin A | 2 IU | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 7.4 mg | 12% |
| Vitamin E | 0.02 mg | 0% |
| Electrolytes | ||
| Sodium | 4 mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 146 mg | 3% |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium | 23 mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0.039 mg | 4% |
| Iron | 0.0.21 mg | 3% |
| Magnesium | 10 mg | 2.5% |
| Manganese | 0.129 mg | 5.5% |
| Phosphorus | 29 mg | 4% |
| Zinc | 0.17 mg | 1.5% |
| Phyto-nutrients | ||
| Carotene-β | 1 µg | -- |
| Cryptoxanthin-β | 0 µg | -- |
| Lutein-zeaxanthin | 4 µg | -- |
Selection and storage
Raw onions can be readily available during all seasons. Depending on the variety, they can be sharp, spicy, tangy, and pungent or mild and sweet. In the stores, they can be available in fresh, frozen, canned, pickled, powdered, and dehydrated forms.
While buying, look for fresh ones that are clean, uniform, well-developed bulbs with dry, flaky outer (tunic) layers. Avoid those that show sprouting or have signs of black mold (a kind of fungal attack) as they indicate that the stock is old. Also, poor-quality bulbs often have split necks, soft spots, moisture at their neck, and dark patches, which may all be signs of decay.
At home, store them in a cool dark place away from moisture and humid conditions where they keep fresh for several days. They can also keep well in the fridge; however, you should use them immediately once you take them out from the fridge since they tend to spoil if kept at room temperature for some time.
Preparation and serving methods
Trim either end using a sharp knife. Then peel the outer 2-3 layers of skin until you find fresh thick pinkish-white whorls. You can slice or cut them into fine cubes depending upon the recipe type. Top greens and flower heads are also edible. Spring onions or scallions are favored in fast-food preparations.
 |
| Delicious pizza with cheese and black olive topping and Cheeseburger with lettuce, tomato, and onion. |
Here are some serving tips:
-
They can be used either chopped or sliced, in almost every type of food, including fresh salads, or as a spicy garnish.
In India and Pakistan, onions are one of the most sought-after ingredients in cooking where they are used in curries, stir-fries, soups, stuffing, paste, dips, sauces, etc., on a regular basis.
They are one of the common ingredients in the Chinese "chow mein" (a kind of recipe with chopped onions, scallions, cabbage, sweet bell peppers, chili and tomato sauce mixture.
They are used extensively in the Mediterranean and continental cooking in salads, cheese pizza, burgers, soup, tarts, rolls, stuffing, etc.
Onions and shallots are some of the common ingredients used extensively in pickling.
Safety profile
Raw onions can cause irritation to the skin, mucosa, and eyes. This effect is because of the release of allyl sulfide gas while chopping or slicing them. The gas, when mixed with moisture (water), converts into sulfuric acid. Allyl sulfide is concentrated more at the ends, especially at its root end. Its effect can be minimized by immersing the trimmed bulb in cold water for a few minutes before you chop or slice it. (Disclaimer).
You may also like to read ≻≻-
Shallots nutrition facts and health benefits.
Spring onion nutrition facts and health benefits.
Leeks nutrition facts and health benefits.
≺≺ Back to Vegetables from Onion nutrition. Visit here for an impressive list of vegetables with complete illustrations of their nutrition facts and health benefits.
≺≺ Back to Home page.
Further reading:
Stanford School of Medicine Cancer information Page- Nutrition to Reduce Cancer Risk (Link opens in new window).